-
- Contact Us
- Privacy Policy
- term and condition
- Cookies policy
1052167-1 SMA Datasheet: Full Specs, Pin Details Guide
Point: SMA-style RF connectors are pervasive in compact RF systems; a working estimate places them as the dominant choice for small-form-factor RF interconnects across telecom, test, and aerospace equipment. Evidence: industry usage studies and procurement tallies repeatedly show SMA-family prevalence. Explanation: engineers and purchasers rely on concise, data-backed references for parts like 1052167-1 to avoid specification mismatches during design and procurement.
Point: This guide explains what to find and how to interpret the official SMA datasheet for 1052167-1. Evidence: the vendor datasheet contains the authoritative electrical, mechanical, and compliance data. Explanation: the article covers full electrical/mechanical specs, detailed pin details and pinout guidance, compatibility and mating notes, PCB and cable design tips, plus pre-purchase and installation checklists to speed validation and reduce field failures. Engineers should refer to the official SMA datasheet for exact numeric values while using this guide to interpret and apply them.
1 — Product background: What is the 1052167-1 SMA connector? (Background introduction)

Part overview and intended applications
Point: 1052167-1 is an SMA-style RF coaxial connector produced for applications requiring reliable, high-frequency interconnection. Evidence: the part family is described in the manufacturer's product literature and official datasheet as an SMA-series coaxial connector with specific mechanical and environmental characteristics. Explanation: intended applications typically include RF test equipment, telecom modules, antenna feeds, and avionics lines where compactness, repeatable performance, and ruggedization (as applicable) are needed. For exact vendor phrasing and marketing blurb, quote the official product blurb from the 1052167-1 datasheet during procurement documentation.
Key differentiators vs. standard SMA variants
Point: 1052167-1 differentiates itself from generic SMA and RP‑SMA variants by mechanical features, finish, and intended mounting style. Evidence: the datasheet lists mechanical modifications, plating notes, and any ruggedization or sealing options that set it apart. Explanation: those differences affect mating compatibility, corrosion resistance, and mechanical durability—critical for aerospace or outdoor telecom use.
| Feature | Standard SMA | 1052167-1 (differentiator) |
|---|---|---|
| Thread / Polarity | Standard 1/4"-36 UNF | Check datasheet for any altered thread profile or polarity variant |
| Ruggedization / Sealing | General use, limited sealing | May include enhanced sealing or retention features—pull exact text from datasheet |
| Plating / Finish | Commonly gold or nickel over brass | Manufacturer-specified plating thickness and corrosion limits—see datasheet |
| Mounting / Interface | Panel or bulkhead variants | Confirm mounting type (bulkhead, PCB, cable) in datasheet |
Quick spec snapshot (at-a-glance)
- Nominal impedance: pull exact value from the official datasheet (commonly 50 ohm for SMA-style parts).
- Frequency range: pull exact from datasheet (datasheet will define guaranteed and usable ranges in GHz).
- Typical VSWR / return loss: pull exact test-condition values and graphs from the datasheet.
- Mating style & mounting type: verify whether bulkhead, PCB-mount, or cable termination and note mating gender.
2 — Full electrical and mechanical specifications (Data deep-dive)
Electrical specs and performance metrics
Point: The datasheet provides definitive electrical parameters: impedance, frequency range, VSWR/return loss, insertion loss, and power rating. Evidence: official specification tables and RF performance graphs in the vendor datasheet contain these values under defined test fixtures and temperatures. Explanation: when assessing the part for a system, engineers must read the datasheet tables and graphs, note test conditions (temperature, fixture, and termination), and ensure the values meet system margins; embed or reference the datasheet tables/plots in design reviews rather than paraphrasing numeric values without context.
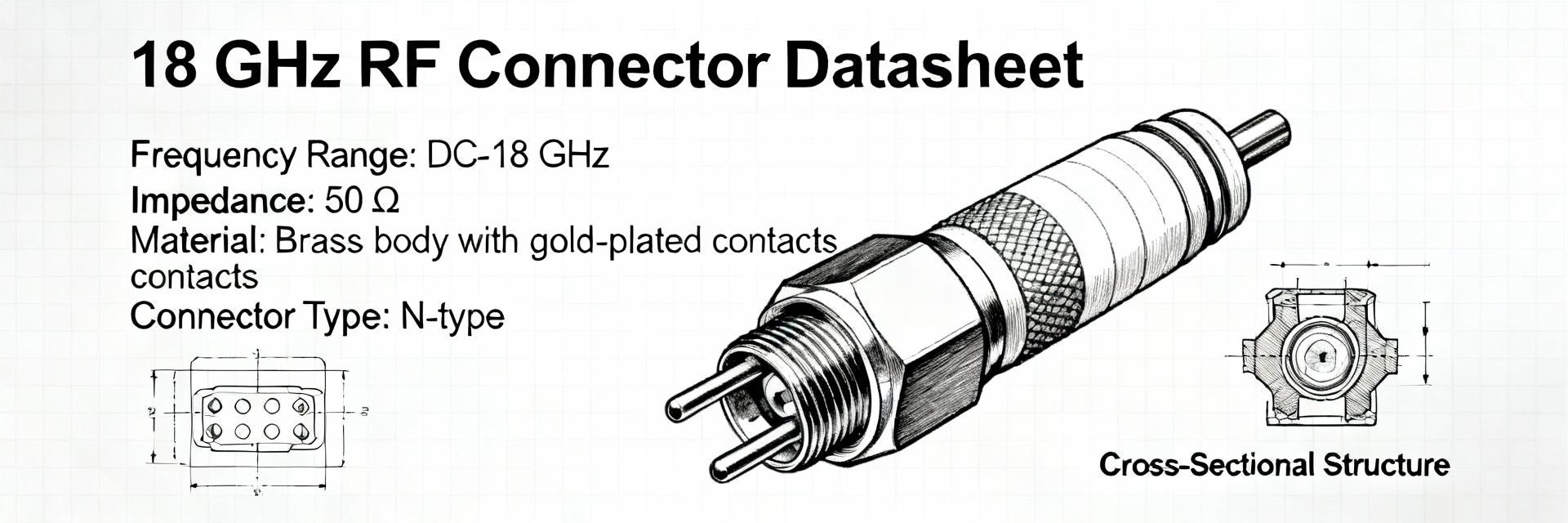
Mechanical dimensions and tolerances
Point: Mechanical drawings and tolerances control fit and PCB footprint compatibility. Evidence: the datasheet dimension tables and mechanical drawings (often with callouts and tolerances) are authoritative. Explanation: designers should capture outer dimensions, thread size, center pin and barrel dimensions, and flange or panel cutout details directly from the datasheet; if MIL‑STD references (for example, a dimensional standard) are cited, copy those citations into the mechanical verification plan and include an SVG/vector for CAD/PCB libraries.
Materials, finishes, and environmental ratings
Point: Contact materials, plating, insulator materials, temperature range, and compliance statements determine suitability for corrosive or high-temperature environments. Evidence: the datasheet lists materials (e.g., contact base metal and plating), insulator type, operating temperature limits, and compliance text (RoHS, MIL compliance if applicable). Explanation: note any stated limitations for corrosive environments or high-temp use, and include the vendor's exact compliance wording in procurement specs rather than paraphrasing.
3 — Pin details & pinout guide (Pin details / Method guide)
Pin numbering, diagram and electrical connections
Point: A clear pin map identifies the center conductor, outer conductor, and any returns or bulkhead grounds. Evidence: the datasheet pin diagram is the canonical source for pin identities and any special notes about isolated or grounded shells. Explanation: recreate or include the datasheet pin diagram in assembly documentation with labeled electrical roles (center = signal, outer = shield/ground) and note any chassis-bonding or insulating features that affect grounding strategy.
Pin dimensions, tolerances and mechanical fit
Point: Exact pin diameters, insertion depths, and plating thicknesses determine mating fit and solderability. Evidence: the datasheet lists pin dimensions and permissible tolerances, sometimes referencing MIL standards for oversize pins or plating thickness. Explanation: capture the pin diameter and tolerance directly from the datasheet and use those figures for pass/fail inspection criteria and for specifying mating pin dimensions to cable vendors or PCB pad designs.
Assembly, soldering and handling notes for pins
Point: Recommended soldering methods, maximum solder temperatures, insertion force, and torque values are in the datasheet and assembly notes. Evidence: manufacturer's assembly notes and handling cautions appear in the datasheet or installation manual. Explanation: follow manufacturer torque and temperature limits; include a do/don't checklist for assembly crews—do verify torque with a calibrated wrench, don't exceed soldering temperatures or dwell times, and don't subject contacts to lateral loads during solder reflow.
- Do: use manufacturer-recommended solder profiles or crimp tooling where applicable.
- Don't: use aggressive fluxes or prolonged high-temperature reflow without confirmation from the datasheet.
4 — Compatibility, mating and application examples (Case studies)
Mating connectors & adapter compatibility
Point: Compatibility depends on thread/polarity and mechanical interface; not all SMA-family parts mate interchangeably. Evidence: datasheet mating instructions and mechanical diagrams define compatible part types. Explanation: list compatible mating types generically (standard SMA male/female, RP variants require polarity checks) and provide vendor-neutral example partner part numbers only after confirming with the datasheet; note that adapters may be required for polarity or gender conversions.
Typical application scenarios and performance expectations
Point: Real-world examples illustrate trade-offs in performance and environment. Evidence: application notes and datasheet performance graphs show expected behavior under defined conditions. Explanation: examples include (1) RF test bench interconnect where repeatability and low VSWR are priority; (2) antenna feed for telecom where sealing and corrosion resistance matter; (3) aerospace avionics where vibration and qualification levels drive ruggedization. For each, verify specified temperature range, vibration qualifications, and mating cycles in the official datasheet before acceptance testing.
PCB footprint and cable assembly design tips
Point: Layout, keepouts, ground vias, and pad dimensions maintain impedance and mechanical stability. Evidence: datasheet mechanical drawings and recommended PCB footprints provide the exact pad sizes and keepout dimensions. Explanation: keep the signal clearance consistent, place perimeter ground vias near the flange for shield return, and follow the datasheet's recommended footprint; for cable assemblies choose controlled-impedance cables and confirm crimp or solder termination details from the manufacturer.
5 — Practical checklist, procurement & troubleshooting (Action guidance)
Pre-purchase checklist (what to verify on the SMA datasheet)
Point: Before ordering, confirm critical attributes to avoid costly mismatches. Evidence: the official 1052167-1 SMA datasheet contains the authoritative values. Explanation: verify the exact part number (1052167-1), nominal impedance, frequency rating, mechanical mounting style, plating/material, environmental ratings, listed mating partners, compliance statements, manufacturer traceability, and lead times. Always include a copy of the relevant datasheet page in the purchase order and ask the vendor for test reports if required.
Installation and inspection checklist
Point: Post-installation inspection reduces early failures. Evidence: torque values, soldering limits, and inspection criteria are defined in the datasheet. Explanation: perform torque verification with calibrated tools, visually inspect pin seating and plating integrity, and run RF verification measurements (return loss, continuity). Use the pass/fail thresholds published in the datasheet or qualification plan; record inspection results to the unit serial for traceability.
Common failure modes and troubleshooting steps
Point: Typical failures include impedance mismatch, intermittent contact, corrosion, and mechanical wear. Evidence: failure analyses and manufacturer troubleshooting notes identify causes and remedies. Explanation: diagnose by measuring return loss and continuity, inspect mechanically for damaged threads or plating, re-torque connectors, and re-terminate or replace if plating or contact springiness is degraded. Log root cause info (mating cycles, environment, applied torque) and replace connectors when repair cannot restore specified electrical performance per the datasheet.
Summary
Point: Accurate interpretation of the official SMA datasheet is essential when using 1052167-1 in critical RF systems. Evidence: the manufacturer’s datasheet is the single source of truth for all electrical, mechanical, and compliance values. Explanation: use this guide to identify which datasheet tables and drawings to extract for procurement, design, and test. Download the official datasheet, verify critical specs listed above for 1052167-1, and contact the vendor for custom questions or test reports.
- Confirm the exact 1052167-1 part designation and mating gender in the SMA datasheet before procurement; mismatched thread/polarity creates immediate functional issues.
- Extract electrical tables (impedance, frequency, VSWR) and embed the exact datasheet graphs into design reviews to validate RF margins.
- Use the manufacturer’s mechanical drawing for PCB footprint and panel cutout; include an SVG/CAD export to maintain dimensional control.
- Follow the datasheet's assembly notes for torque, solder profile, and environmental limits; use pass/fail criteria from the datasheet for inspection and test.
Frequently Asked Questions
What electrical values should I extract from the 1052167-1 SMA datasheet?
Point: Only extract the datasheet's official electrical tables and graphs. Evidence: the datasheet lists nominal impedance, guaranteed frequency band, VSWR/return loss curves, insertion loss, and power handling under stated test conditions. Explanation: copy those values verbatim into system specifications and note the test fixture and temperature used; do not rely on third-party summaries for critical margin calculations—always reference the datasheet's original tables.
How do I confirm pin details for 1052167-1 before PCB layout?
Point: Verify pin diameters, insertion depth, and pad geometry from the official drawing. Evidence: the datasheet mechanical drawing with pin callouts is the authoritative source. Explanation: incorporate the exact footprint into the PCB CAD library as a vector; include recommended keepouts and ground via placement from the datasheet to preserve shielding and mechanical clearance.
When is replacement required versus repair for a worn 1052167-1 connector?
Point: Replacement is required when electrical performance falls outside datasheet limits or when mechanical damage is evident. Evidence: acceptance criteria and mating cycle life are described in the manufacturer's documentation. Explanation: if return loss or continuity tests fail relative to datasheet thresholds, or plating and contact springiness are visibly compromised, replace the connector rather than attempt field repair; log mating cycles and environmental exposure as part of the root-cause report.
- Technical Features of PMIC DC-DC Switching Regulator TPS54202DDCR
- STM32F030K6T6: A High-Performance Core Component for Embedded Systems
- APT50GH120B Datasheet Deep Dive: Specs, Ratings & Curves
- APT50GH120BSC20 Power Module: Latest Performance Report
- APT50GH120BD30 IGBT: How to Maximize Efficiency for EV Drive
- GTSM20N065: Latest 650V IGBT Test Report & Metrics
- CMSG120N013MDG Performance Report: Efficiency & Losses
- GTSM40N065D Technical Deep Dive: 650V IGBT + SiC SBD
- NOMC110-410UF SO-16: Live Stock & Price Report
- 1757255 MSTBA 5.08mm PCB: Step-by-Step Install & Solder
-
 EXB-V4V120JVPanasonic Electronic ComponentsRES ARRAY 2 RES 12 OHM 0606
EXB-V4V120JVPanasonic Electronic ComponentsRES ARRAY 2 RES 12 OHM 0606 -
 EXB-V4V473JVPanasonic Electronic ComponentsRES ARRAY 2 RES 47K OHM 0606
EXB-V4V473JVPanasonic Electronic ComponentsRES ARRAY 2 RES 47K OHM 0606 -
 EXB-V4V823JVPanasonic Electronic ComponentsRES ARRAY 2 RES 82K OHM 0606
EXB-V4V823JVPanasonic Electronic ComponentsRES ARRAY 2 RES 82K OHM 0606 -
 EXB-V4V151JVPanasonic Electronic ComponentsRES ARRAY 2 RES 150 OHM 0606
EXB-V4V151JVPanasonic Electronic ComponentsRES ARRAY 2 RES 150 OHM 0606 -
 EXB-V4V181JVPanasonic Electronic ComponentsRES ARRAY 2 RES 180 OHM 0606
EXB-V4V181JVPanasonic Electronic ComponentsRES ARRAY 2 RES 180 OHM 0606 -
 EXB-V4V331JVPanasonic Electronic ComponentsRES ARRAY 2 RES 330 OHM 0606
EXB-V4V331JVPanasonic Electronic ComponentsRES ARRAY 2 RES 330 OHM 0606 -
 EXB-V4V152JVPanasonic Electronic ComponentsRES ARRAY 2 RES 1.5K OHM 0606
EXB-V4V152JVPanasonic Electronic ComponentsRES ARRAY 2 RES 1.5K OHM 0606 -
 EXB-V4V563JVPanasonic Electronic ComponentsRES ARRAY 2 RES 56K OHM 0606
EXB-V4V563JVPanasonic Electronic ComponentsRES ARRAY 2 RES 56K OHM 0606 -
 EXB-V4V104JVPanasonic Electronic ComponentsRES ARRAY 2 RES 100K OHM 0606
EXB-V4V104JVPanasonic Electronic ComponentsRES ARRAY 2 RES 100K OHM 0606 -
 EXB-V4V154JVPanasonic Electronic ComponentsRES ARRAY 2 RES 150K OHM 0606
EXB-V4V154JVPanasonic Electronic ComponentsRES ARRAY 2 RES 150K OHM 0606